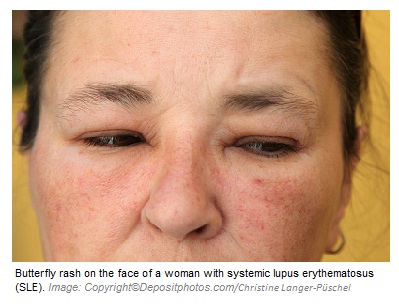
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease with unknown cause
and characterized by a butterfly-shaped skin rash on the face and involvement of multiple organs (vessels, kidneys, gastrointestinal system, blood, musculoskeletal system, heart, lungs, joints, skin, and nervous system). It is a chronic inflammatory disorder.
People with SLE may complain of fever, low level of energy, weakness, muscle and joint pain, hair loss, headaches, and depression. SLE could manifest at any ages in both genders. However, it is eight to ten times more common in young women of childbearing age than in men.
Potential risk factors:
- Autoimmunity.
- Genetics.
- Hormones.
- Environmental factors: pollution and industrial emissions.
- Drugs: hydralazine, procainamide, methyldopa, chlorpromazine, isoniazid, phenytoin, and quinidine. They may cause a SLE-like syndrome.
- Food allergies.
- Oxidative stress.
- Toxic chemicals.
- Nutritional deficiencies, especially vitamin A, beta-carotene, and vitamin E.
Nutritional Supports:
Restricted Foods:
- Saturated fats.
- Trans-fats.
- Processed foods.
- Fried foods.
- Sugars and sweets. They weaken immune system.
- Foods high in gluten: wheat, breads, oats, rye, barley, semolina, spelt, kamut, couscous, and triticale.
- Foods high in solanine: potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, and peppers. Solanine is a poisonous plant alkaloid produced by the plants from nightshade family as a natural defense mechanism against external microorganisms. Solanine exacerbates inflammation.
- Foods high in Omega-6: soy, sunflower oil, safflower oil, corn oil, borage oil, sesame oil, and evening primrose oil. Omega-6, particularly Alpha-Lioleic Acid, is a pro-inflammatory.
- Inflammatory foods: red meats, eggs, and dairy products.
- Alcohol.
- Coffee.
- Allergenic foods. The most common allergenic foods in SLE are wheat, corn, red meats, eggs, citrus fruits, soy, and peanuts.
Recommended Foods:
- Plenty of water: at least 2 liters a day.
- Gluten free foods: brown rice, quinoa, buckwheat, and millet.
- Legumes.
- Cold water fish: salmon, and mackerel.
- Flaxseeds.
- Chia seeds.
- Hemp seeds.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables, except allergenic and solanine-containing ones.
- Fruits high in flavonoids: berries, and red grapes.
- Ginger.
- Pineapple.
- Spices high in antioxidants: sumac, turmeric, and cinnamon.
Recommended Supplements:
- DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone): 25 – 75 mg a day. DHEA may improve SLE symptoms.
- Omega – 3 Fatty Acids: 2 -3 grams a day.
- French Maritime Pine Bark Extract: 200 – 300 mg a day.
- Grape Seed Extract: 100 – 200 mg a day.
- Curcumin: 1000 – 1500 mg a day.
- Co – Enzyme Q10: 200 – 300 mg a day. It is an antioxidant that increases energy level.
- Vitamin E: 400 – 800 IU a day.
- Bromelain: 1500 mg a day.
- Digestive Enzymes: A full spectrum product.
- Probiotics: A product that provides 5 to 10 billion active organisms per serving.
- White Willow Bark: 400 – 800 mg a day. It contains salicin that reduces pain and inflammation.
- Vitamin B5: 1000 – 2000 mg a day.
- Multivitamins – Multiminerals: A high potency product.
Miscellaneous Suggestions:
- Liver detoxification.
- Colon cleansing.

