Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the skin characterized by sharply 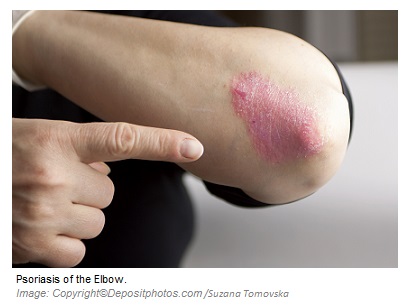 circumscribed reddened plaques covered by silvery scales.
circumscribed reddened plaques covered by silvery scales.
The skin lesions are either asymptomatic or itchy. Affecting about 1% of people, psoriasis is most often localized on the scalp, extensor surfaces of the elbows and knees, sacrum, buttocks (commonly the gluteal cleft), back of the neck, and genitals. Other involved regions include the nails, eyebrows, axillae, and umbilicus. The lesions follow alternating periods of exacerbation and remission.
Up to 30% of people with psoriasis develop arthritis (psoriatic arthritis). Moreover, lesions of psoriasis usually appear in traumatic areas, which is called “Koebner`s or isomorphic phenomenon”. It is seen in 30 – 50 % of people with psoriasis.
Potential triggering and contributing factors:
- Genetics.
- Stress.
- Infections.
- Trauma, such as scratching the skin, X – ray, sunburn, vaccination, and surgery.
- Hormonal imbalances, such as in pregnancy, and acromegaly.
- Climate: topical and humid weather heals the lesions and cold and dry weather exacerbates them.
- Metabolic disorder, such as hypoglycemia.
- Poor liver function.
- Leaky gut syndrome.
- Medications: beta-blockers, lithium, anti-malarial drugs, alpha-interferon, gamma-interferon, ACE inhibitors, and some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (such as indomethacin).
- Dietary factors:
- Diets low in fiber.
- Diets high in protein.
- Poor digestion.
- Dysbiosis (imbalance of normal flora).
- Nutritional deficiencies, such as vitamins D and A, zinc, essential fatty acids, and antioxidants.
- Food allergies.
Nutritional Supports:
Restricted Foods:
- Saturated fats.
- Hydrogenated fats.
- Fried foods.
- Processed foods.
- Sugars and sweets.
- High protein diet.
- Alcohol.
- Caffeine.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Caffeinated beverages.
- Gluten – containing foods: wheat, breads, oats, rye, barley, semolina, spelt, kamut, couscous, and triticale.
- Foods high in solanine: potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, and peppers. Solanine is a poisonous plant alkaloid produced by the plants from nightshade family as a natural defense mechanism against external microorganisms. Solanine exacerbates inflammation.
- Foods high in Omega-6: soy, sunflower oil, safflower oil, corn oil, borage oil, sesame oil, and evening primrose oil. Omega-6, particularly Alpha-Lioleic Acid, is a pro-inflammatory.
- Inflammatory foods: red meats, eggs, and dairy products especially milk.
Recommended Foods:
- Water: at least 2 liters a day.
- Foods high in fiber: legumes, avocado, artichoke, and pears.
- Foods high in zinc: legumes and pumpkin seeds.
- Gluten free diets (see “Celiac Disease”).
- Fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Foods high in Omega-3: fish, flaxseeds, walnuts, chia, and hemp seeds.
- Foods high in flavonoids: berries, and red grapes.
- Vegetables with liver detoxifying effects: broccoli, beets, and dandelion.
- Foods high in vitamin A: sweet potatoes, carrots, paprika, chili pepper, cayenne, butternut squash, dark green leafy vegetables, apricot, and cantaloupe.
- Foods high in carotenoids (see “Carotenoids” under the section “Phytonutrients”).
- Figs: they contain psoralen that help with psoriasis.
- Ginger.
- Turmeric.
- Chamomile tea.
Recommended Supplements:
- Fumaric Acid: 100 – 120 mg a day, and gradual increase to 500 mg a day over several weeks. It is naturally produced in the skin upon exposure to sun and may improve psoriatic symptoms.
- Omega – 3 Fatty Acids: 2 – 3 grams. These essential fatty acids reduce inflammation and improve symptoms.
- French Maritime Pine Bark Extract: 200 – 300 mg a day. This powerful flavonoid reduces inflammation, improves blood circulation and supports immune system.
- Grape Seed Extract: 100 – 200 mg a day.
- Curcumin: 1000 – 1500 mg a day. It is a power antioxidant extracted from turmeric powder that has an inflammatory effect and improves liver function.
- Aloe Vera Juice: ½ cup three times a day. It provides different nutrients and improves healing of the lesions.
- Folic Acid: 1000 mcg a day. Caution: do not take folic acid if you are taking the medication methotrexate.
- Vitamin B12: 1000 mcg a day.
- Vitamin D: 3000 – 5000 IU a day.
- Zinc: 50 – 100 mg a day.
- Milk Thistle Extract (containing 80% silymarin): 600 – 900 mg a day. It has a liver detoxifying effect.
- Betaine Hydrochloride: 300 – 600 mg with each meal. It helps with digestion of proteins.
- Dandelion Extract: Dandelion root: as a dried form, 5 – 15 grams a day, or as a tincture 10 – 30 ml day. It contains taraxacin that improves digestion and increases bile production.
- Sarsaparilla: as a capsule, 1500 – 2000 mg a day, or as a tincture 10 – 15 ml a day. This herb contains a saponin called sarsasapogenin and also beta-sitosterol. They have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Digestive Enzymes: A full spectrum product.
- Probiotics: A product that provides 5 to 10 billion organisms per serving.
- Multivitamins – Multiminerals: A high potency product.
Topical Implications:
- Capsaicin cream: apply two to three times a day onto the lesions. It reduces pain and itching.
- Calendula cream: apply two to three times a day onto the affected areas. Calendula contains flavonoids, saponins, and carotenoids that reduce inflammation and itching, and improves healing.
- Aloe vera gel: apply two to three times a day onto the skin lesions. It has a healing effect.
- Chickweed cream: apply two to three times a day. It reduces itching and inflammation.
- Witch hazel cream: apply two to three times a day onto the skin lesions. Tannins and volatile oils in witch hazel have anti-inflammatory effects.
Miscellaneous Suggestions:
- Liver detoxification.
- Whole body detoxification.
- Colon cleansing.
- Sunbathing.
- Stress management.
- Aromatherapy with lavender.
- Constitutional hydrotherapy.

