The gallbladder is a pear-shaped and distensible sac located underneath the 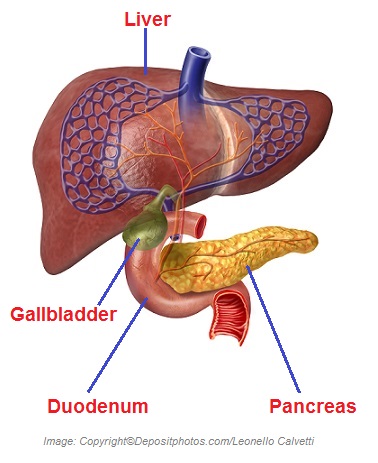 liver. Its functions are (a) storing and concentrating bile acids and (b) contracting and releasing bile acids into the upper part of the small intestine as a part of digestion process. Two common disorders of the gallbladder are cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) and cholelithiasis (gallstones).
liver. Its functions are (a) storing and concentrating bile acids and (b) contracting and releasing bile acids into the upper part of the small intestine as a part of digestion process. Two common disorders of the gallbladder are cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) and cholelithiasis (gallstones).
Cholecystitisis inflammation of the gallbladder characterized by abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, fever, chill, nausea, and vomiting. Severe cases maybe associated with jaundice and shock.
Potential contributing factors are:
- Gallstones.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Sickle cell anemia.
- Gender: females more than males.
- Severe burns.
- Postpartum period after a prolonged labor.
- Prolonged TPN (total parenteral nutrition).
- Gallbladder cancer.
- Parasitic infestation of the gallbladder.
- Sarcoidosis.
- Tuberculosis.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Syphilis.
- Systemic fungal infections.
Gallstones are the most common disorder of the gallbladder. They are formed due to abnormal bile composition. The two major types of gallstones are cholesterol stones (80%) and pigment stones (20%). Many persons with gallstones usually have no symptoms. They become symptomatic by causing gallbladder inflammation or blocking the bile duct, which leads to biliary colic.
Potential contributing factors are:
- Obesity.
- Gender: females more than males.
- Old age.
- Dietary factors:
- Weight loss.
- Fasting.
- TPN (total parenteral nutrition).
- High calories intake.
- High fat diet.
- Pregnancy.
- Birth control pills.
- Genetics.
- Medications: octreotide, tamoxifen, clofibrate, ceftriaxone, and statins.
- Medical conditions:
- Pernicious anemia.
- Alcoholic liver cirrhosis.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Bacterial and parasitic infections of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
- Crohn`s disease.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Metabolic syndrome.
Nutritional Supports:
Restricted Foods:
- Saturated, hydrogenated, and Trans – fats.
- Sugars and sweets.
- Fried foods.
- Processed foods.
- Margarine.
- Red meats.
- Sodas.
- Alcohol.
- Foods with glycemic index over 55, such as cakes, pastries, cookies, muffins, doughnuts, white breads, and dressings.
- High fat dairy products.
- Eggs.
- Beef liver.
- Artificial sweeteners.
- Foods additives, preservatives, and colorings.
- Allergenic foods.
- Caffeinated drinks.
Recommended Foods:
- Drink plenty of water: at least 2 liters a day.
- Whole grains.
- Foods high in fiber: lentils, beans, avocado, oats, and artichoke.
- Foods high in omega-3: fish, flaxseeds, chia, and hemp seeds.
- Fruits and vegetables high in flavonoids: berries, red grapes, grapefruit, pomegranate, sea buckthorn, persimmon, kiwi, beets, basil, garlic, parsley, radish, radicchio, rhubarb and parsnips.
- Beets.
- Dandelion greens.
- Foods with GI less than 55 (see “Glycemic Index“ unde the section of “Carbohydrates“).
- Nuts.
- Spices: cinnamon, turmeric, oregano, basil, cayenne, sumac, and rosemary.
- Ginger.
- Turmeric.
- Chlorella and spirulina.
- Fruits and vegetables high in phytosterols: acai berry, goji berry, lemon, persimmon, plum, sea buckthorn, strawberry, alfalfa sprouts, amaranth, avocado, beets, bell pepper, cabbage, celery, cucumber, eggplant, onion, tomatoes, turnip, turnip greens, and yams.
- Green tea.
Recommended Supplements:
- French Maritime Pine Bark Extract: 200 – 300 mg a day. It is a potent antioxidant that reduces inflammation and improves blood circulation.
- Grape Seed Extract: 100 – 200 mg a day.
- Curcumin: 1000 – 1500 mg a day. It is a powerful antioxidant that detoxifies the liver.
- Milk Thistle Extract (containing 80% silymarin): 600 – 900 mg a day. It has a liver detoxifying effect and improves bile flow.
- Betaine Hydrochloride: 600 – 1200 mg a day. It helps people with poor digestion and low gastric acid secretion.
- Dandelion Extract: Dandelion root: as a dried form, 5 – 15 grams a day, or as a tincture 10 – 30 ml day. It contains taraxacin that improves digestion, increases bile production, and has a laxative effect.
- Vitamin C: 1000 – 3000 mg a day.
- Lecithin (Phosphatidylcholine): 500 – 1000 mg a day. It increases the solubility of cholesterol in bile.
- Artichoke Extract: 500 – 1000 mg a day. An active compound of artichoke is cynarine, which stimulates biliary secretion and improves the function of the gallbladder.
- PGX: 3000 – 4500 mg a day. It is a water-soluble fiber that helps lower blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
- Digestive Enzymes: A full spectrum product.
- Probiotics: a product that provides 15 to 20 billion organisms per serving.
- Vitamin B – Complex: A high potency product

