Eczema is inflammation of the skin characterized by a dry, red, inflamed, scaly, and itchy
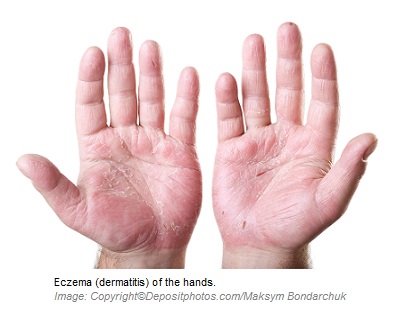 skin. It may be associated with an increased thickening of the skin and even infection of the skin. Eczema could manifest from infancy to adulthood. In severe cases, it leads to crusting, flaking, blistering, cracking, oozing, and even bleeding of the affected areas.
skin. It may be associated with an increased thickening of the skin and even infection of the skin. Eczema could manifest from infancy to adulthood. In severe cases, it leads to crusting, flaking, blistering, cracking, oozing, and even bleeding of the affected areas.
Atopic Dermatitis (AD) is a common eczema of infancy and childhood, affecting 3 – 5% of children before 5 years of age. Being considered as an allergic disease, eczema is mainly seen in the front of the wrists and elbows, neck, face, and the back of the knees and hands.
Potential contributing factors:
- Genetics.
- Food allergies.
- Stress.
- Immune system abnormalities.
- Irritants (metals, soaps, perfumes, and topical medications).
- Exposure to sun.
- Poor digestion.
- Nutritional deficiencies.
- Disordered body detoxification.
- Bacterial overgrowth in the intestines.
- Abnormal metabolism of essential fatty acids.
- Industrial and household chemicals.
- Fungal overgrowth.
Nutritional Supports:
Restricted Foods:
- Saturated fats.
- Trans-fats.
- Processed foods.
- Fried foods.
- Sugars and sweets. They weaken the immune system.
- Foods high in gluten: wheat, breads, oats, rye, barley, semolina, spelt, kamut, couscous, and triticale.
- Foods high in linoleic acid (a type of Omega-6 fatty acid): safflower, sunflower, sesame, and grape seed oils. Linoleic acid is a pro-inflammatory.
- Inflammatory foods: red meats, eggs, and dairy products.
- Alcohol and coffee.
- Allergenic foods. The most common allergenic foods are dairy products, eggs, peanuts, soybeans, citrus fruits, chocolate, wheat, tomatoes, eggplants, and shellfish.
- Additives, preservatives, and food colorings.
- MSG (monosodium glutamate)-containing foods.
- Spicy foods.
Recommended Foods:
- Plenty of water: at least 2 liters a day.
- Gluten free foods: brown rice, quinoa, buckwheat, and millet.
- Legumes.
- Cold water fish: salmon, herring, and mackerel.
- Flaxseeds.
- Chia seeds.
- Hemp seeds.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Fruits high in flavonoids: berries, and red grapes.
- Fruits and vegetables high in beta-carotene: green leafy and orange-colored vegetables.
- Ginger.
- Spices high in antioxidants: sumac, turmeric, and cinnamon.
- Chamomile and peppermint teas.
Recommended Supplements:
- Omega – 3 Fatty Acids: 2 – 3 grams a day.
- French Maritime Pine Bark Extract: 200 – 300 mg a day.
- Grape Seed Extract: 100 – 200 mg a day.
- GLA (gamma linoleic acid): 300 – 600 mg a day. It has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Evening Primrose Oil: 3000 mg a day. It contains GLA.
- Vitamin E: 400 – 800 IU a day.
- Bromelain: 1500 mg a day. It reduces inflammation.
- Quercetin: 1500 – 3000 mg a day. It has an anti-inflammatory affect.
- Digestive Enzymes: A full spectrum product.
- Probiotics: a product that provides 5 to 10 billion active organisms per serving.
- White Willow Bark: 400 – 800 mg a day. It contains salicin that reduces inflammation.
- Vitamin A: 2000 – 5000 IU a day.
- Milk Thistle (with 70 – 85% silymarin): 400 – 500 mg a day. It supports liver detoxification.
- Aloe Vera Juice: ¼ to ½ cup three times a day. It has internal and external healing effects.
- Zinc: 50 -100 mg a day.
- Multivitamin – Multiminerals: A high potency product.
Topical Implications:
- Calendula cream: apply two to three times a day onto the affected areas. Calendula contains flavonoids, saponins, and carotenoids that reduce inflammation and itching, and improves healing.
- Aloe Vera gel: apply two to three times a day onto the skin lesions. It has a healing effect.
- Chamomile lotion: apply one to two times a day.
- Red clover cream: apply one to two times a day onto the skin lesions.
- Chickweed cream: apply two to three times a day. It reduces itching and inflammation.
- Witch hazel cream: apply two to three times a day onto the skin lesions. Tannins and volatile oils in witch hazel have anti-inflammatory effects.
Miscellaneous Suggestions:
- Liver detoxification.
- Colon cleansing.

