Citrulline is a nonessential amino acid and is not usually a constituent of proteins.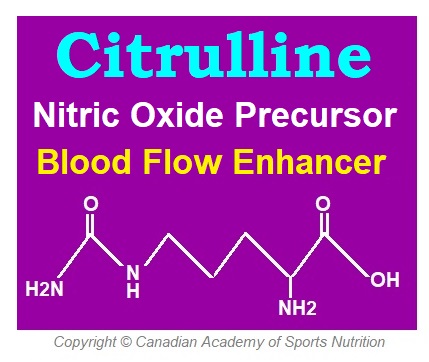 It was called citrulline as it was first isolated from watermelon. Citrullus is the Latin word for watermelon. Citrulline is a naturally occurring substance made in the body as a part of urea cycle, which mainly takes place in the liver and kidneys. It is especially found in the blood, hair and skin.
It was called citrulline as it was first isolated from watermelon. Citrullus is the Latin word for watermelon. Citrulline is a naturally occurring substance made in the body as a part of urea cycle, which mainly takes place in the liver and kidneys. It is especially found in the blood, hair and skin.
Citrulline is made in the body either from the amino acid ornitine by adding carbon dioxide or directly from the amino acid arginine catalyzed by nitric oxide synthase (NOS). The inter-conversion of citrulline and arginine generates a molecule named nitric oxide (NO). In a nutshell, the functions of citrulline are: a) to elevate the production of nitric oxide in the body, which is a potent vasodilator and enhances blood flow, b) to promote the removal of ammonia from the body, and c) to boost the immune system.
Athletic Benefits:
As a nitric oxide precursor, citrulline may benefit athletes through the followings:
1) Enhances blood flow to the exercising muscles.
2) Augments ATP production.
3) Delays fatigue and exhaustion by increasing reabsorption of lactic acid.
4) Helps with exercise-induced muscle growth.
5) Aids with post-exercise recovery.
Non-Athletic Benefits:
The following medical conditions may benefit from citrulline: 
6) Compromised immune system.
Dosage and Side Effects:
Citrulline is available as pill or powder in the form of citrulline malate. Most formulations contain citrulline and malate with the ratio of 2:1 for better function. It may be mixed with other amino acids especially arginine. Citrulline is a component of many pre-exercise products.
Citrulline malate can be used before, during and after exercise. The daily dose varies from 2 to 10 grams. Citrulline is considered safe and no side effects have been reported.
There is a medical condition called “citrullinemia“. It is a genetic metabolic disorder in which the blood levels of citrulline, arginine and ammonia are elevated in the blood. It is a rare condition with citrullinemia type II being mostly common in Japan. People with citrullinemia are at greater risk to develop liver cancer.
There is no correlation between citrulline supplementation and liver cancer in healthy individuals.
Interactions:
Citrulline may have the following interactions:
1) Viagra and Cialis: citrulline may increase their effectiveness, causing blood pressure to drop significantly.
2) Nitrate medications: citrulline may increase their effectiveness, causing blood pressure to drop significantly.

