 contents of the stomach move back into the esophagus resulting in symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, nausea, increased saliva (water brash), bad breath, and belching. The process of moving the stomach contents back into the esophagus is referred to as reflux.
contents of the stomach move back into the esophagus resulting in symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, nausea, increased saliva (water brash), bad breath, and belching. The process of moving the stomach contents back into the esophagus is referred to as reflux.
Some symptoms are not related to gastrointestinal tract and they include chronic cough, laryngitis, asthma, and dental erosions.
In general, the stomach contents should not move back into the esophagus. Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is an anatomical ring at the junction of esophagus and stomach that prevents reflux. Any problems with the LES would lead to GERD. However, function of the LES is sometimes abnormal.
Complications of GERD in the long term are chronic esophagitis (bleeding and narrowing), esophageal cancer, and Barrett`s esophagus.
Barrett`s esophagus is a condition in which the cells at the lower portion of the esophagus are replaced by different types of cells. This process is known as metaplasia (Barrett`s metaplasia). People with Barrett`s esophagus are 20 times more at risk for developing esophageal cancer than others. According to medical books, the rate of developing a cancer in Barrett`s esophagus is about 0.5% per year.
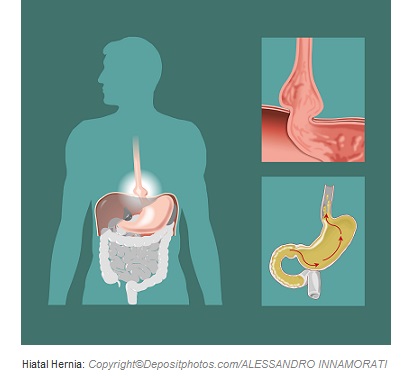
A common cause of GERD is hiatal hernia. Hiatal hernia is protrusion and herniation of the upper part of the stomach into the chest through the diaphragmatic hiatus.
Potential contributing factors for developing GERD:
- Hiatal hernia.
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure.
- Obesity.
- Scleroderma.
- Pregnancy.
- Increased secretion of stomach acid.
- Delay in gastric emptying.
- Disorders in esophageal peristalsis.
- Zollinger – Ellison syndrome.
- Smoking.
- Alcohol.
- Gluttony.
- Nutritional factors: fatty foods, caffeinated and carbonated beverages.
- Drugs: antihistamines, anti-cholinergics, tricyclic antidepressants, nitrates, calcium channel blockers, corticosteroids, birth control pills, narcotics, nicotine patches, asthma medications, tranquilizers such as Valium, Advil, aspirin, iron supplements, potassium supplements, and tetracycline antibiotics
Nutritional Supports:
Restricted Foods:
- Fatty foods: butter, margarine, sausage, bacon, cheese and sauces.
- Processed meats.
- Tomato and tomato-based foods such tomato paste, tomato juice, and pasta sauce.
- Fried foods: French fries.
- Potato chips.
- Cream cheese.
- Whipped cream.
- Omelets and scrambled eggs.
- Onion and onion rings.
- Chicken wings and skins.
- Garlic.
- Egg rolls.
- Doughnuts.
- Peppermint.
- Spearmint.
- Minty foods.
- Chocolate.
- Alcohol.
- Coffee and tea.
- Caffeinated and carbonated beverages.
- Spicy foods.
- Citrus fruits.
Recommended Foods:
- Plain water: at least 2 liters a day. Water can dilute stomach acid and reduce symptoms.
- Whole grains.
- Fresh fruits and vegetables except citrus fruits.
- Flaxseeds.
- Flaxseed oil.
- Low fat dairy products.
- Pineapple.
- Papaya.
- Fruits and vegetables high in mucilage: jujube, aloe vera, chia seeds, flaxseeds, kelp, marshmallow, okra, and psyllium. Mucilage is a glycoprotein that has healing and anti-inflammatory activities in the gastrointestinal system by covering the mucous membranes and protecting them from getting irritated.
- Chamomile tea.
- Ginger.
Recommended Supplements:
- Licorice in the form of DGL (de-glycyrrhizinated licorice): 200 – 300 mg tablet chewed before each meal and before bed. Licorice alleviates irritation and heals inflammation.
- Aloe Vera Juice: ¼ – ½ cup three times a day. It has soothing and healing effects.
- Digestive Enzymes: A full spectrum product.
- Probiotics: take a product that provides 5 to 10 billion organisms per serving.
- Bladderwrack: as capsules 200 – 600 mg a day, as tincture 2 – 3 ml a day, or as a tea 1 teaspoon of dried form per one cup of hot water for three times a day. It is a type of seaweed with active ingredients iodine, alginic acid and fucoidan that soothes heartburn and heals gastritis and esophagitis.
- Slippery Elm Bark: as a dried form 2 – 4 grams a day, or as a tincture 9 – 12 ml a day. Slippery elm contains mucilage that soothes heartburn and speeds up healing.
- Gentian Root Extract: as a capsule, 100 – 200 mg about 15 minutes before each meal, or as a tincture, 10 drops about 15 minutes before each meal. Gentian contains the glycosides gentiopicrin and amarogentin that help with digestion.
Miscellaneous Suggestions:
- Avoid overeating.
- Avoid eating within 3 hours before bedtime.
- Do not lie down right after eating. Stay in upright position up to 45 – 60 minutes after eating.
- Elevate the head of your bed 5 – 10 inches when lying down.
- Weight loss in obese people.
- Stop smoking.

