 and by non-athletes to extend their life span, elevate sexual drive, and increase their stamina are growth hormone and testosterone.
and by non-athletes to extend their life span, elevate sexual drive, and increase their stamina are growth hormone and testosterone.
For detailed information about growth hormone, see “GH Enhancers”.
Testosterone is the body`s main androgenic hormone, and is secreted from the testes, ovaries, and adrenal glands. In men, about 95% of testosterone is produced in the testes and 5% by the adrenal glands, whereas it is synthesized by the adrenal glands and ovaries in women.
The pituitary gland, the master gland of the body, controls the synthesis and secretion of testosterone by releasing two hormones called LH (luteinizing hormone) and FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone). They are called gonadotropins. The pituitary gland itself is under the control of the hypothalamus; it secretes GnRH, which makes the pituitary gland to release LH and FSH. As well, testosterone in the blood can control its secretion from the testes by exerting a negative feedback effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
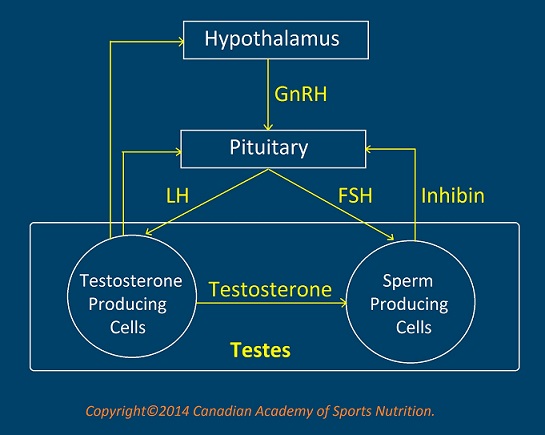

LH hormone works mostly on Leydig cells of the testes, which produce steroids especially testosterone. FSH is responsible mainly for the production of sperm and semen. There is a complicated relationship between these two processes, the production of sperm and the synthesis of testosterone. FSH can also increase the secretion of testosterone and testosterone is necessary for sperm production and their maturation. Growth hormone reinforces the effect of testosterone on the testes, whereas estrogens reduce it.
The body makes testosterone from cholesterol. The diagram below shows the chemical synthesis of testosterone and other hormones.
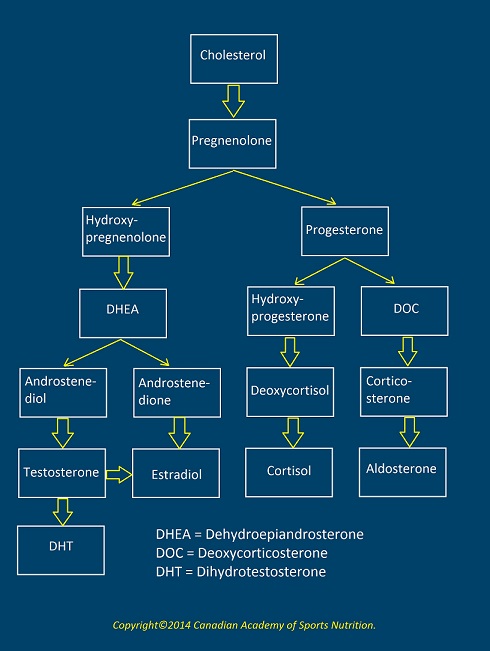

Normal Secretion of Testosterone:
Normal daily secretion of testosterone in men is about 7 mg, which is approximately 20 to 30 times more than that in women. Testosterone is mainly produced by the testes in adult men, whereas it is secreted by the adrenal glands and ovaries in women. Normal daily production of testosterone in women is 0.25 mg, of which half is due to conversion of androstendione to testosterone in other body`s tissues. The blood level of testosterone in women is about 15 to 65 nanograms per deciliter, but normal range of testosterone in men is 250 to 1000 nanograms per deciliter.
Testosterone level is relatively high during three periods of the male life cycle: fetal period, infancy, and adulthood. The level of testosterone begins to increase in the males after the eighth week of pregnancy and diminishes before birth. Afterward, its level increases again and reduces after being in a high level for several months. Testosterone level is low during prepubescent period (it is about 20 nanograms), and then increases sharply during adulthood. There is a normal decline in both males and females in testosterone secretion with aging.
Mechanism of Action:
About 98% of testosterone, the predominant masculinizing androgen in the body, is bound to proteins in the blood stream after being secreted. Only 1 to 2 percent of testosterone is unbounded or free, which is the biologically active form of testosterone. There arebiologically important small oscillations in the secretion of testosterone.Oscillations follow an equal number of pulses of GnRH secretion by the hypothalamus and LH from the pituitary.
Testosterone circulates within the blood to reach the target organs. In the majority of tissues, testosterone is converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a metabolic product of testosterone, which is more potent in some tissues. The half-life of testosterone is approximately 90 minutes, which means that one-half of the body`s total testosterone is destroyed by the liver every 90 minutes. Conversion of testosterone to DHT mainly occurs in the prostate gland, hair follicles, and external genitalia. About 20% of DHT is produced by the adrenal glands. On the other hand, an enzyme named “aromatase”, converts testosterone to estrogen. Some food supplements increase testosterone levels by inhibiting aromatase.
Effects of Testosterone:
Testosterone itself is somewhat inactive within the target organs, and most of its androgenic effects are exerted via DHT. Testosterone is responsible for both androgenic and anabolic (tissue building) effects. Here is a list of the androgenic and anabolic effects of testosterone:
– Controls sexual differentiation in the fetus.
– Influences on the production of sperm.
– Develops secondary male sex characteristics.
– Is essential for the development of the internal and external genital systems and for their optimal functions.
– Is necessary for the development of pubic and axillary hair in both males and females.
– Increases the size of the larynx and deepens the voice.
– Affects sexual behavior.
– Increases muscle mass and strength by elevating protein synthesis.
– Accelerates growth spurts, directly by influencing on the end plates of the long bones, and indirectly by stimulating growth hormone secretion, which thenstimulates IGF-Iproduction. Testosterone promotes protein anabolism and growth and enhances linear bone growth and muscular development; consequently, it increases height.
– Elevates the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen and nutrients within the body.
– Can increase sebaceous gland activity, which may result in acne.
Indications for Use:
Some medical reasons for using testosterone are as follows:
1) Replacement therapy for low function of the testes and pituitary gland.
2) Accelerate growth and promote anabolism.
3) Stimulate the production of red blood cells in resistant anemia.
4) Treatment of osteoporosis.
5) Palliative therapy in breast cancer that has spread to distant sites.
6) Adjuvant therapy in patients with short stature.
7) Treatment of hereditary angioneurotic edema.
8) Stimulation of maturity in cases of delayed puberty.
Contraindications for the use of testosterone include advanced breast cancer that has not spread to distant sites, prostate cancer, liver diseases, and high blood levels of calcium.
Side Effects and Toxicity:
The most common adverse reactions of testosterone are edema, jaundice, local irritation, urinary obstruction, and steroid fever. In women who use testosterone, the most important side effect is masculinization—the development of male characteristics such as a deepened voice and the growth of facial hair. Following consumption of testosterone, the secretion of gonadotropins (LH and FHS) is suppressed and consequently the women experience irregularity in menstruation. Male baldness, an increase in the body`s hair and enlargement of the clitoris occur in women in long-term use.
The most significant side effect of too much testosterone in men is gynecomastia (breast enlargement); its exact mechanism is unknown. Other adverse effects in men include prostate enlargement, priapism (painful erection of the penis), reduction in the number of sperm and infertility in advanced cases, and low and high sexual drive.
Toxic effects of testosterone in both sexes are edema and water retention, early closure of growth plates in children and consequently, short stature, increased levels of blood calcium, alteration in the blood levels of cholesterol, and liver dysfunction. A dangerous side effect is liver dysfunction, which results in complications varying from mild jaundice to liver cancer. Oral forms of testosterone have more side effects, especially on the liver, than injection and patch forms do.
Testosterone Declines with Aging:
When you grow older, a gradual decline in testosterone levels occurs. Testosterone loss  starts in the late forties. Reduction of testosterone levels produce a series of symptoms; the most common of them are changes in sexual function such as loss of libido, difficulty with erection and maintaining it, and sexual dissatisfaction. Other symptoms include low stamina, fatigue, depression, depressed moods, joint stiffness, irritability, and decreased immune system function.
starts in the late forties. Reduction of testosterone levels produce a series of symptoms; the most common of them are changes in sexual function such as loss of libido, difficulty with erection and maintaining it, and sexual dissatisfaction. Other symptoms include low stamina, fatigue, depression, depressed moods, joint stiffness, irritability, and decreased immune system function.
The aforementioned symptoms can be managed by maintaining testosterone in high levels through the use of food supplements and exercise programs. By keeping testosterone levels in high profile, you will be able to restore your libido, elevate your mood, increase your stamina, increase your bone density, and feel youthful.

