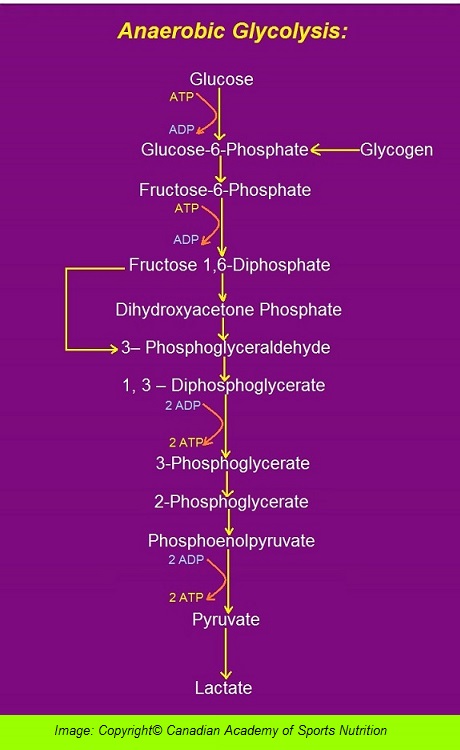
the main provider of ATP during intense exercise that lasts 10 – 120 seconds. As an exercise continues more than 10 seconds, the anaerobic glycolytic system takes charge of providing ATP. This system uses glucose in the blood or glycogen to form ATP rapidly without oxygen. If glucose is used, it generates 2 ATPs, while if glycogen is used, it forms 3 ATPs.
The end product of this energy system is lactic acid. As lactic acid accumulates, the production of ATP via anaerobic glycolysis starts declining. This system provides ATP for up to 2 – 3 minutes. If exercise continues beyond 2 – 3 minutes, either the intensity of exercise should be decreased or the body would switch to aerobic systems to use oxygen to produce ATP.

Sports with Dominating Anaerobic Glycolysis System
The anaerobic glycolysis system is the dominant energy system in the following sports:
- Athletics:
- 200 m dash.
- 400 m dash.
- 800 m dash.
- 400 m hurdles.
- 4X400 m relay.
- Badminton.
- Canoe/Kayak:
- Slalom events (all events).
- Sprint, women`s events (all events).
- Sprint, men`s events (C-1 200 m canoe single, K-1 200 kayak single, and K-2 200 kayak double).
- Cycling, BMX events.
- Football (soccer).
- Gymnastics: acrobatic events (all events).
- Handball.
- Hockey (ice).
- Luge.
- Rugby 7.
- Skating:
- Speed skating (1500 m, 1000 m, 500 m).
- Short track speed skating (1500 m, 1000 m, 500 m).
- Skiing:
- Alpine skiing (all events).
- Freestyle skiing (half-pipe, moguls, slope style).
- Snowboarding (half-pipe, giant parallel slalom, parallel slalom, slope style, snowboard cross).
- Cross – country skiing (sprint, 1.5 km).
- Swimming:
- Freestyle swimming (50 m, 100 m, 4X100 m relay).
- Backstroke swimming (100 m).
- Breaststroke swimming (100 m).
- Medley swimming (4X100 m relay).
- Taekwondo.
- Tennis.
- Water polo.
- Wrestling.